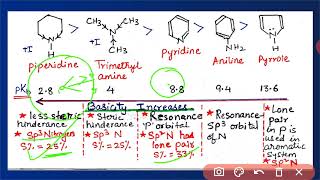
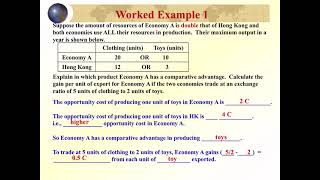
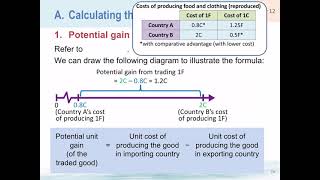
Duration 2:16
Comparative Study on Metal Segregation of Bimetallic Nanocatalysts Prepared by a One-Pot Method
Published 24 Jun 2021
Comparative Study on Metal Segregation of Bimetallic Nanocatalysts Prepared by a One-Pot Method in Microemulsions A comparative study on different bimetallic nanocatalysts prepared from microemulsion using a one-pot method has been carried out. The analysis of experimental observations, complemented by simulation studies, provides detailed insight into the factors affecting nanoparticle architecture: 1.- The metal segregation in a bimetallic nanocatalysts is the result of the combination of three main kinetic parameters: the reduction rate of metal precursors (related to reduction standard potentials), the material intermicellar exchange rate (determined by microemulsion composition) and the metal precursors concentration. 2.- A minimum difference between the reduction standard potentials of the two metals of 0.20 V is needed to obtain a core-shell structure. For values De° smaller than 0.20 V the obtaining of alloys cannot be avoided, neither by changing the microemulsion nor by increasing metal concentration. 3.- As a rule, the higher the film flexibility around the micelles, the higher the degree of mixture in the nanocatalyst. 4.- A minimum concentration of metal precursors is required to get a core-shell structure. This minimum concentration depends on the microemulsion flexibility and on the difference in reduction rates.
Category
Show more
Comments - 0